29
Jan
Diamond Cut
- Imagine a diamond, and you no doubt think ‘sparkle’. Well, that sparkle comes from the way the diamond is cut. Cut is often confused with the shape of the diamond but in fact they are two different aspects of the stone. Shape refers to the overall outline of a diamond when viewed from above. Examples include princess, emerald, marquise, oval, pear, heart and cushion which are referred to as fancy shapes.
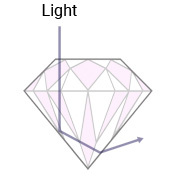
- Cut, on the other hand refers to the way the stone interacts with light. It is an indication of the quality of the facets, symmetry and dimensions which have been cut into the rough diamond and polished to give sparkle and maximize brilliance.
- Most diamonds, though, are round and the facets are cut and polished to show off the brilliance of the stone. A round brilliant diamond displays 58 facets, 33 on the crown and 25 on the pavilion, for maximum sparkle.

- A well-cut diamond will display three aesthetic properties; brilliance, dispersion and scintillation. Light which hits the diamond and reflects off it is known as brilliance. As light enters the diamond, some of the rays are ‘dispersed’ leading to flecks of colored light known as ‘fire’. When a diamond is moved, these colors move too. This phenomenon is known as scintillation. So, aesthetically, it could be argued that cut is more important than carat



RELATED
Posts
18
Jan
Diamond Format
Diamonds are formed deep within the Earth's mantle under conditions of extreme pressure and temperature. The process of diamond formation and the time it...
read more
18
Jan
Natural Diamond
Diamonds have a rich and fascinating history that spans thousands of years. Here’s an overview of their journey from ancient times to the present:
Ancient...
read more
19
Jan
Natural Diamond Process
Diamonds are formed deep within the Earth's mantle and brought to the surface through volcanic eruptions. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of the diamond formation...
read more
19
Jan
THE 4 C's OF DIAMONDS
When it comes to diamonds, there are four universally accepted characteristics that grade diamonds. They are referred to as the 4C’s of Diamonds: Carat,...
read more
20
Jan
Diamond Mines Around The World
Africa
Jwaneng Mine (Botswana)
Orapa Mine (Botswana)
Venetia Mine (South Africa)
Catoca Mine (Angola)
Cullinan Mine (South Africa)
Letseng Mine (Lesotho)
Karowe Mine (Botswana)
Marange Fields (Zimbabwe)
Russia
Jubilee (Yubileyny) Mine (Sakha Republic)
Mir Mine...
read more
21
Jan
Diamond Carat
Diamond weight is measured in carats, a small unit of measurement equal to 200 milligrams. Each carat is divided into 100 points. Therefore, a...
read more
23
Jan
Diamond Clarity
Most diamonds have unique clarity characteristics, much like a fingerprint. These distinguishing characteristics can be classified as inclusions and blemishes. Inclusions are enclosed within...
read more
25
Jan
Diamond Colour
Generally, the less color a diamond has, the more valuable it is. Natural diamonds have a wide range of colors ranging from completely colorless...
read more

